Efficient IoT Communication: MQTT vs. LwM2M Protocols
Comparing the Energy Efficiency and Device Management Capabilities of MQTT and LWM2M in IoT Implementations
Understanding MQTT and LwM2M for IoT
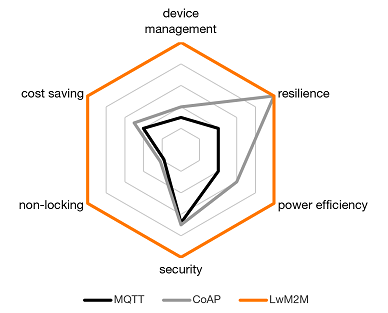
When it comes to Internet of Things (IoT) implementations, choosing the right communication protocol is crucial for device management and overall efficiency. Two of the prominent protocols in the IoT are MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) and LwM2M (Lightweight Machine to Machine). While MQTT is known for its message transport capabilities, LwM2M stands out for its comprehensive device management features.
MQTT: The Message Transporter
MQTT is a protocol designed for message transport. It’s particularly useful for scenarios where a small code footprint is required and network bandwidth is at a premium. However, MQTT is often criticized for being “chatty”, which can lead to inefficiencies, especially on high-latency networks such as NB-IoT. This chattiness can result in higher power consumption, making it less ideal for energy-sensitive applications.
LwM2M: The Device Management Expert
In contrast, LwM2M is a device management protocol that provides a full-fledged solution for IoT devices. It includes an expandable data model and capabilities for remote device management, such as advanced telemetry data management and firmware update mechanisms. LwM2M operates over UDP, making it resilient and suitable for global deployments across various network technologies. Its intelligent session management and advanced data transmission mechanisms can lead to significant energy savings—up to three times less power consumption compared to MQTT, as reported by Adeunis.
Comparative Analysis and Energy Efficiency
A comparative analysis by IEEE1 highlights some differences between MQTT and LwM2M. The study notes that LwM2M is slightly less efficient than MQTT for sending messages larger than 800 bytes. However, it does not account for the energy savings achieved by LwM2M’s ability to maintain a connection without needing to reconnect to the server after standby periods. This feature can lead to substantial energy savings compared to MQTT, which requires reconnection before communication with the platform.
The Long-Term Benefits
While the IEEE study provides valuable insights, it overlooks the cumulative long-term benefits of using LwM2M. By implementing the energy-saving mechanisms provided by the LwM2M standard, organizations can optimize their IoT implementations for better energy efficiency over time. This optimization is crucial for large-scale deployments where energy consumption can significantly impact operational costs and sustainability goals.
So what should you choose?
Choosing between MQTT and LwM2M depends on the specific needs of your IoT project. If your priority is efficient message transport for devices with limited power resources, LwM2M’s robust device management and energy-saving features make it a compelling choice. For more detailed insights, the IEEE’s comparative analysis provides an in-depth look at the protocols’ performance across different phases of communication.
1 A. Parmigiani and U. Dettmar, “Comparison and Evaluation of LwM2M and MQTT in Low-Power Wide-Area Networks,” 2021 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence Systems (IoTaIS), Bandung, Indonesia, 2021, pp. 8-14, doi: 10.1109/IoTaIS53735.2021.9628463. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9628463

 B2B "IoT enthusiasts" group
B2B "IoT enthusiasts" group Tutorials
Tutorials Orange Business
Orange Business